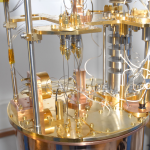
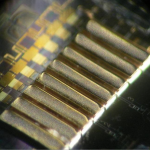
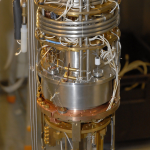
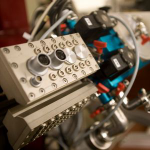
- Photon Transport in a Bose-Hubbard Chain of Superconducting Artificial Atoms
G. P. Fedorov et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 126, 180503 (2021) - Path-Dependent Supercooling of the
He3 Superfluid A-B Transition
Dmytro Lotnyk et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 126, 215301 (2021) - Superconductivity in an extreme strange metal
D. H. Nguyen et al., Nat Commun 12, 4341 (2021) - High-Q Silicon Nitride Drum Resonators Strongly Coupled to Gates
Xin Zhou et al., Nano Lett. 21, 5738-5744 (2021) - Measurement of the 229Th isomer energy with a magnetic micro-calorimeter
T. Sikorsky et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 125 (2020) 142503
Dynamical similarity and instabilities in high-Stokes-number oscillatory flows of superfluid helium
D. Schmoranzer, M. J. Jackson, Š. Midlik, M. Skyba, J. Bahyl, T. Skokánková, V. Tsepelin, L. SkrbekWe present a unified analysis of the drag forces acting on oscillating bodies submerged in superfluid helium such as a vibrating wire resonator, tuning forks, a double-paddle oscillator, and a torsionally oscillating disk. We find that for high-Stokes-number oscillatory flows, the drag force originating from the normal component of superfluid helium exhibits a clearly defined universal scaling. Following classical fluid dynamics, we derive the universal scaling law and define relevant dimensionless parameters such as the Donnelly number. We verify this scaling experimentally using all of our oscillators in superfluid 4He and validate the results by direct comparison with classical fluids. We use this approach to illustrate the transition from laminar to turbulent drag regime in superfluid oscillatory flows and compare the critical velocities associated to the production of quantized vortices in the superfluid component with the critical velocities for the classical instabilities occurring in the normal component. We show that depending on the temperature and geometry of the flow, either type of instability may occur first and we demonstrate their crossover due to the temperature dependence of the viscosity of the normal fluid. Our results have direct bearing on present investigations of superfluids using nanomechanical devices [Bradley et al., Sci. Rep. 7, 4876 (2017)].
Phys. Rev. B 99, 054511 (2019)
doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.99.054511
arxiv: http://www.research.lancs.ac.uk/portal/en/publications/-(8f5c10a7-e5d5-4a2f-b0a0-7ad5563dc4f3).html
supplemental material: http://dx.doi.org/10.17635/lancaster/researchdata/264