Administration of EMP-related Publications
| year | 2011 |
| author(s) | D.I. Bradley, S.N. Fisher, A.M. Guenault, R.P. Haley, G.R. Pickett, D.Potts, V. Tsepelin |
| title | Direct measurement of the energy dissipated by quantum turbulence |
| document type | Paper |
| source | Nature Phys. 7, 473 (2011) |
| doi | 10.1038/nphys1963 |
| EMP/Horizon2020 | This publication does not include a EMP/Horizon2020 acknowledgement. |
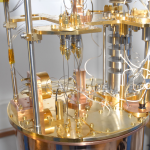
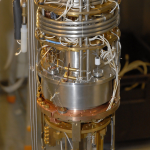
| abstract | The lack of a general solution to the governing Navier–Stokes equations means that there is no fundamental theory of turbulence. In the simpler case of pure quantum turbulence, the tangle of identical singly quantized vortices in superfluids at T~0 may provide a deeper understanding of turbulence in general. The well-known Kolmogorov theory predicts the energy distribution of turbulence and how it decays. In normal systems the turbulent energy is generally only a small perturbation on the total thermal energy of the supporting medium. In quantum turbulence, however, the energy is accessible. A stationary condensate is necessarily in its ground state with zero enthalpy. Thus quantum turbulence accounts for the entire free energy of the superfluid and there are no other contributions. Here, we exploit this property to make the first direct measurement of the energy released by freely decaying quantum turbulence. Our results are consistent with a Kolmogorov energy spectrum with an inferred Kolmogorov constant remarkably similar to those of classical fluids. |